Editor’s note: This article was updated on March 16, 2022.
In this story, you'll learn:
Increased emissions of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO2) are changing our planet’s climate. The effects of climate change will negatively impact billions of humans, but it is possible to mitigate these effects. Companies can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by switching to renewable energy and improving efficiency in their production processes. Four examples from around the world demonstrate how we’re saving energy at our factories worldwide.
Climate change is a crisis with potentially dramatic consequences for everybody on Earth. That’s why individuals and organizations around the globe must take decisive action to tackle it immediately. In this spirit, the United Nations has set a clear target for limiting the rise in our planet’s temperature as part of the Paris Agreement on Climate Change. Henkel recognizes the serious challenges presented by a warming planet and has set specific targets for itself to help mitigate negative impacts from climate change – starting with our commitment to converting our production sites to a climate-positive C02 balance by 2030. In addition to climate change, rising energy costs, resource scarcity and evolving regulatory landscapes make energy efficiency a key contributor to the future of business. This global challenge is also an opportunity to save costs, reduce CO2 emissions and increase productivity. Henkel aims to cut its CO2 footprint by 65 percent by 2025 in comparison to the base year 2010. We’re taking steps to reduce energy consumption at all of our sites worldwide, include designing sustainable factories, retrofitting existing plants with smart technologies, switching to renewable energy, and unlocking the potential of smart factories.
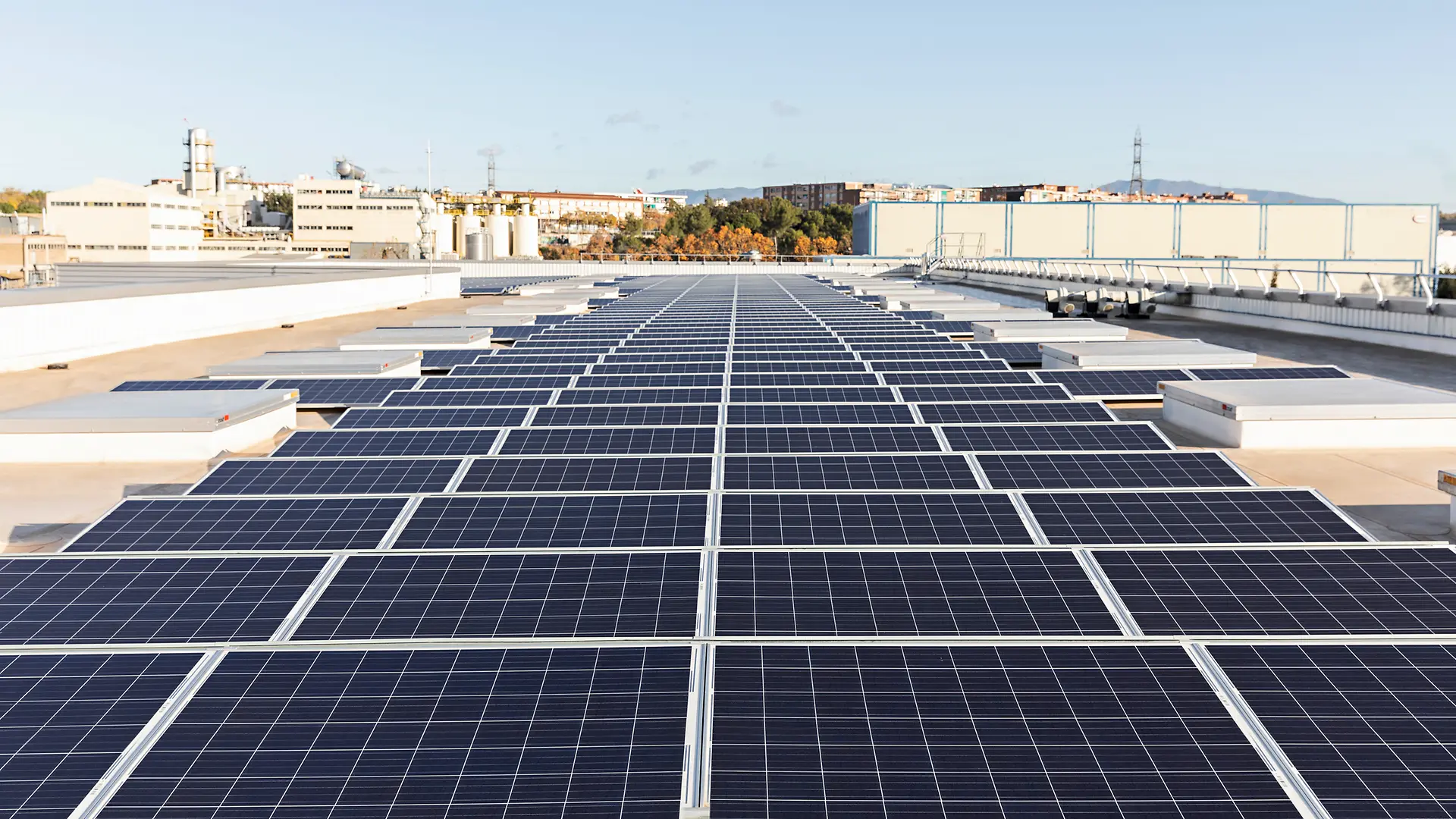
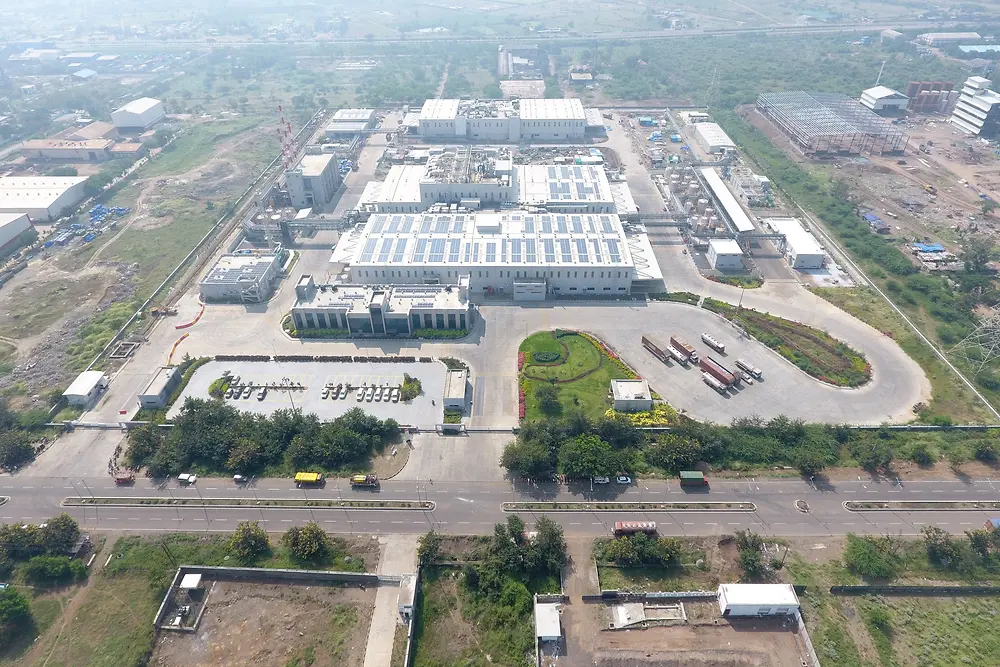
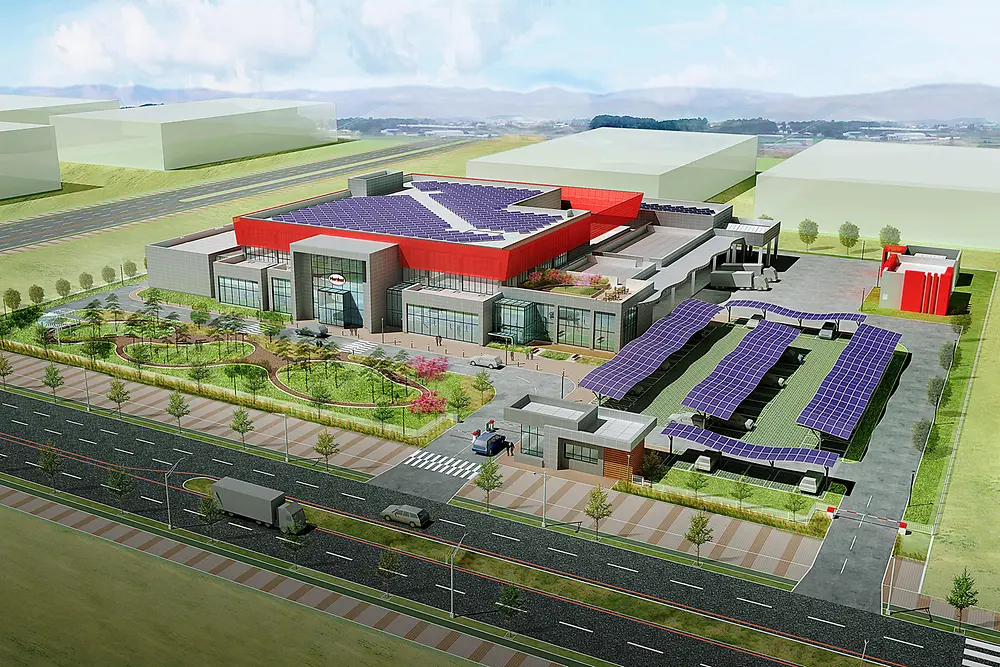
Increasing energy efficiency at our production sites begins when we design new factories. Our factory in Kurkumbh, India, was designed as a smart factory. It enables a wide range of Industry 4.0 operations and meets the highest standards for sustainability. The site layout was developed in line with lean manufacturing concepts that organize material flows in the best possible way to increase productivity, minimize waste and cut emissions. Alongside highly efficient equipment, it uses digital technology to optimize processes, and features smart systems for ventilation, air conditioning and lighting. The roof is covered by 7,000 square meters of solar panels that generate more than 1,000,000 kilowatt hours of energy and save around 800 tons of CO2 each year. Plans are in place to add more panels and purchase additional solar power from an external provider. In recognition of its energy-efficient design, the factory is one of only a handful of chemical manufacturing sites in the world that have received the LEED Gold certificate from the US Green Building Council.